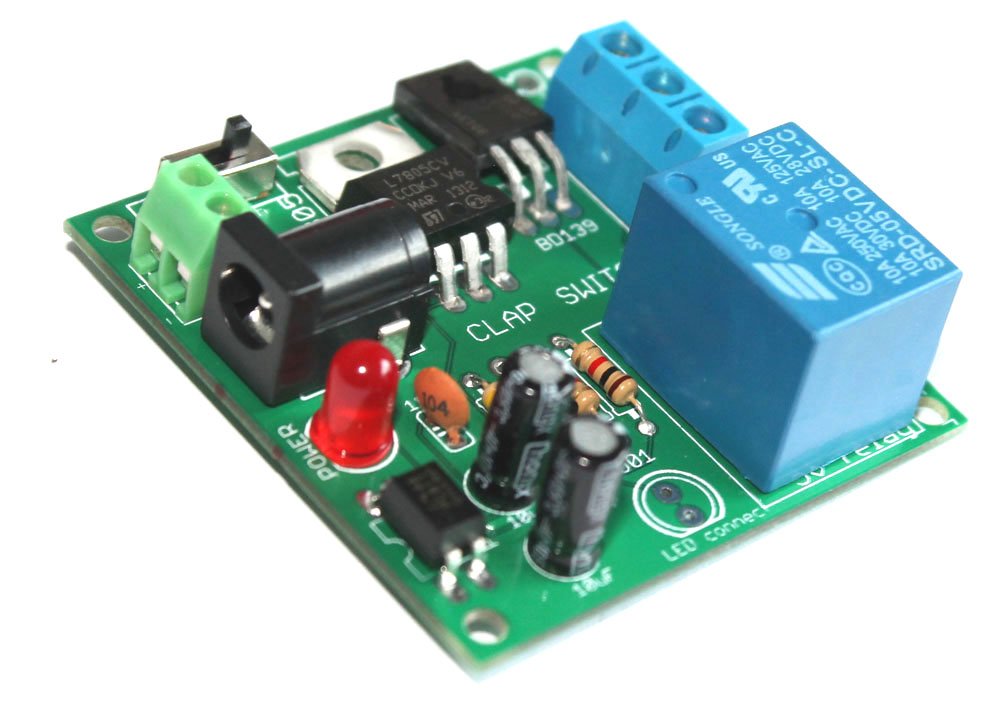
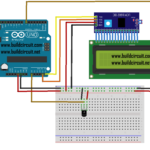
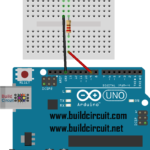
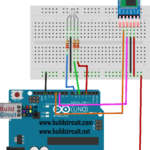
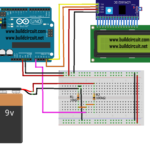
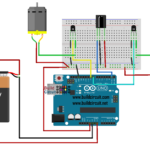
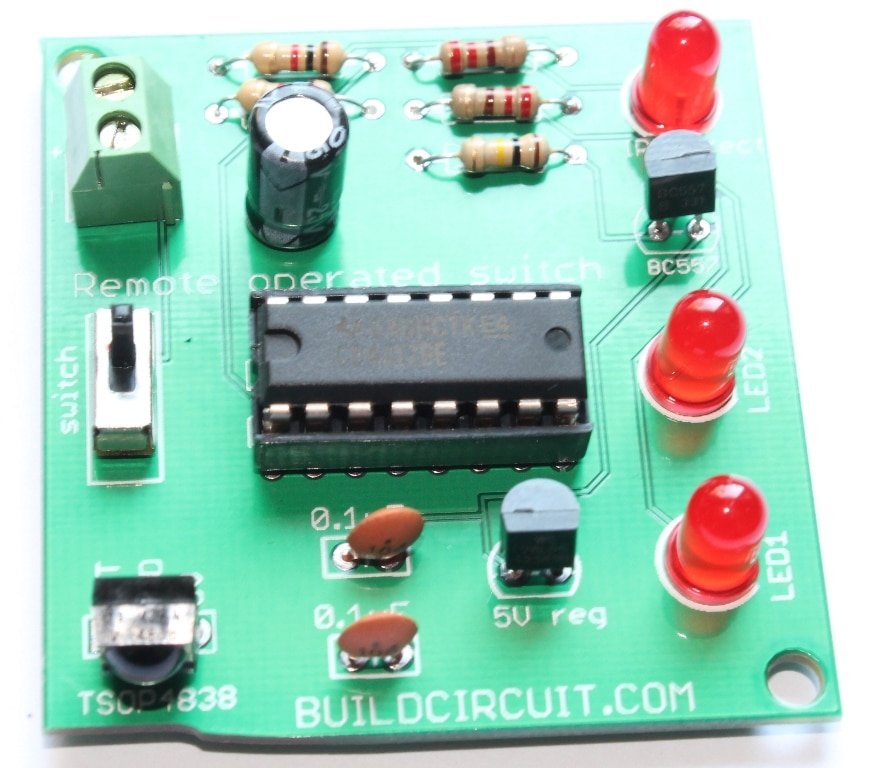
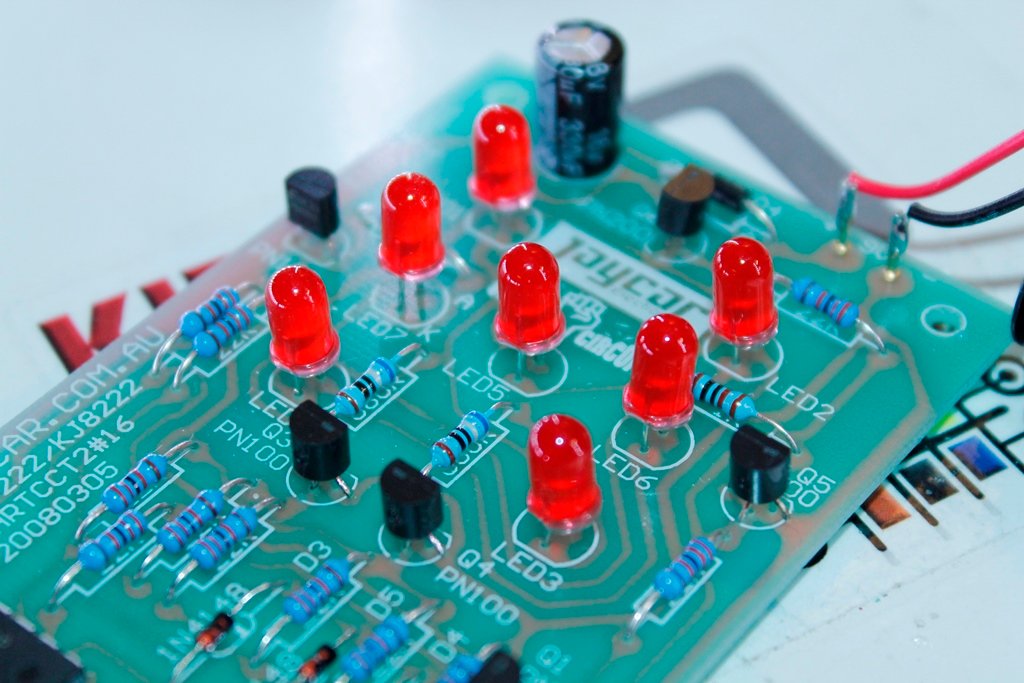
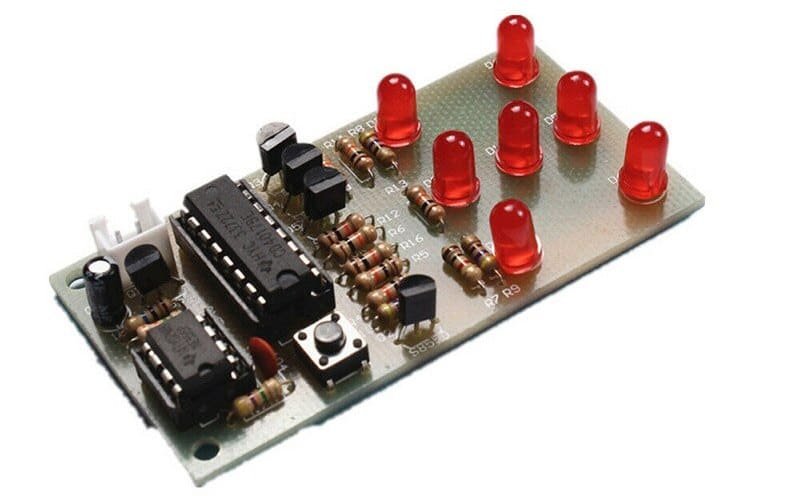
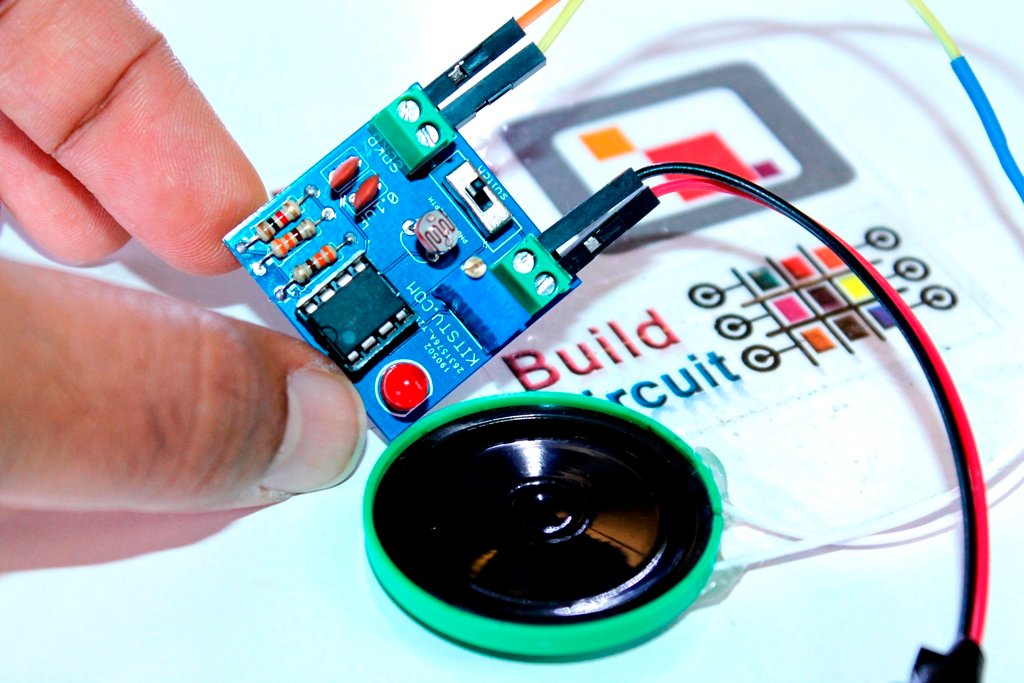
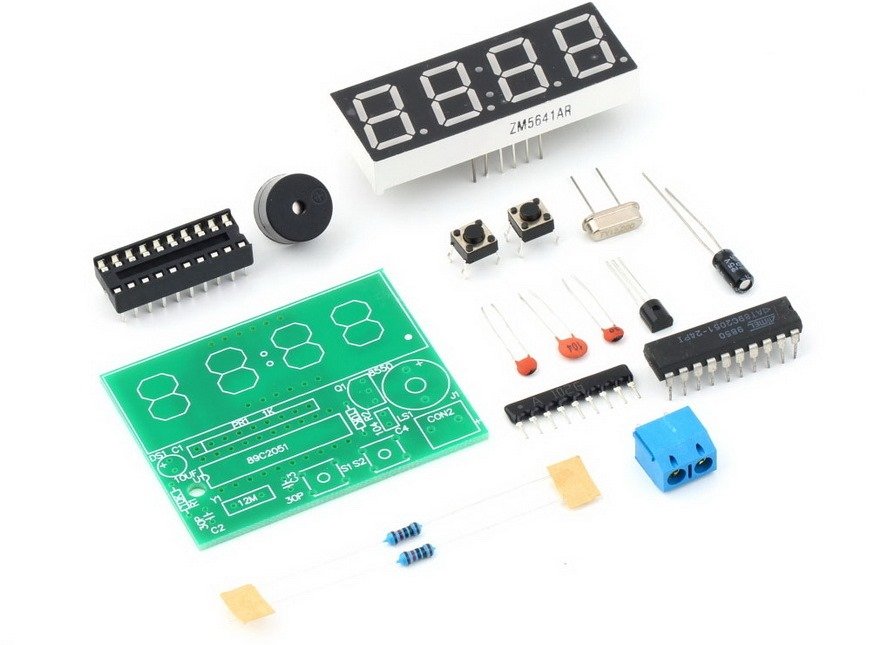
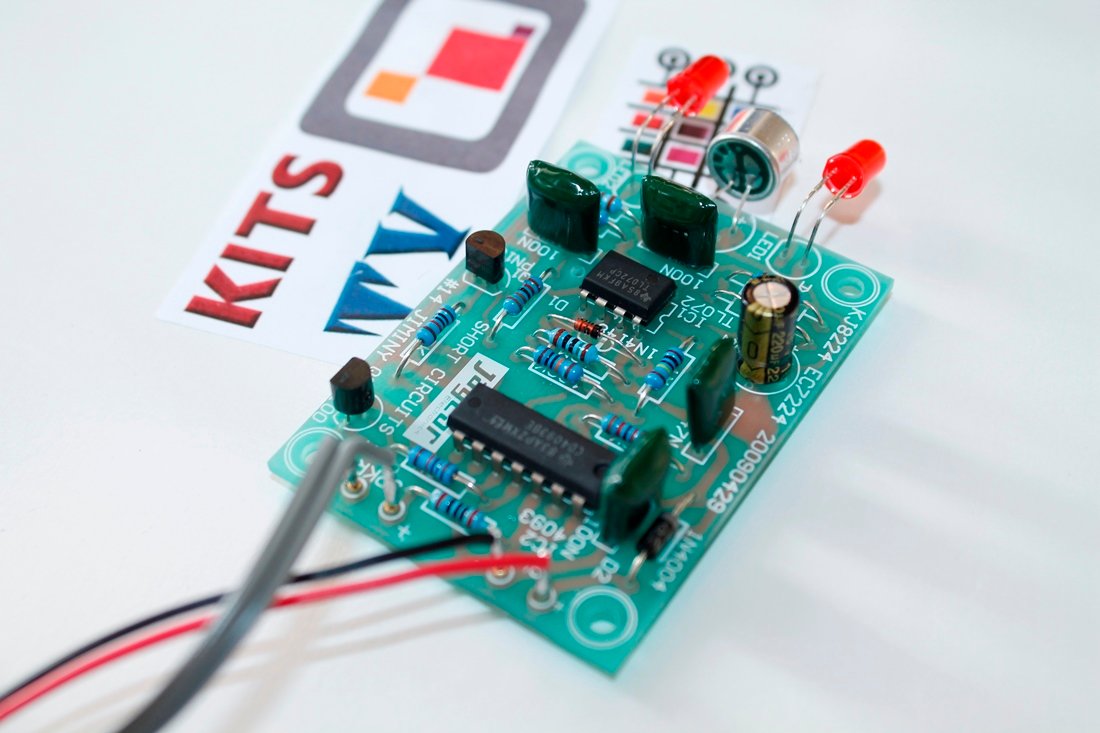
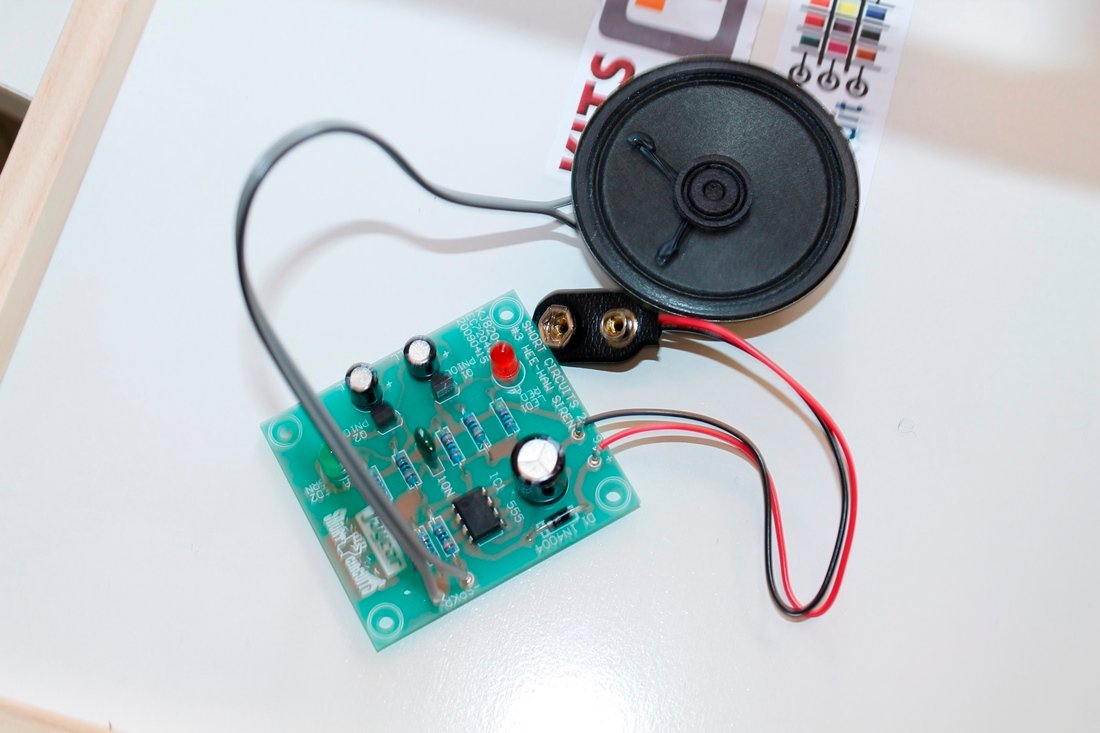
How to connect the relay module to the popular clap switch
This article strictly focuses on how to connect the relay-module to the popular clap-switch. If you have come to this page from a search engine, we recommend you to visit the following pages: 1. About Relay module for the popular clap_switch (Get description of this kit) 2. How to connect clap-switch to the relay…