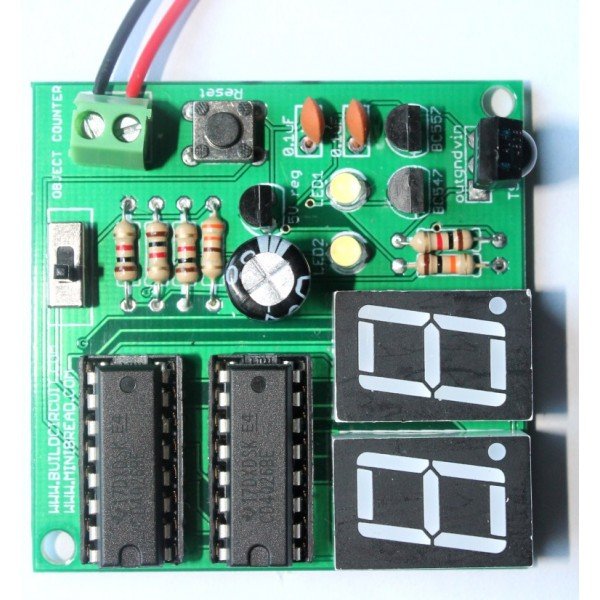
Digital object counter DIY kit
🛠️ Dive into our collection of DIY Kits, 🔊 Audio Amplifiers, Digital Scoreboards, FM transmitters, and more! 🎶 Explore endless possibilities at our new store.
🛠️ Dive into our collection of DIY Kits, 🔊 Audio Amplifiers, Digital Scoreboards, FM transmitters, and more!
🎶 Explore endless possibilities at our new store.

🛠️ Dive into our collection of DIY Kits, 🔊 Audio Amplifiers, Digital Scoreboards, FM transmitters, and more! 🎶 Explore endless possibilities at our new store.

🛠️ Dive into our collection of DIY Kits, 🔊 Audio Amplifiers, Digital Scoreboards, FM transmitters, and more! 🎶 Explore endless possibilities at our new store.

Two digits – Digital object counter DIY kit is one of the most popular kits designed by BuildCircuit. The kit is very popular among electronics beginners and intermediate circuit players.
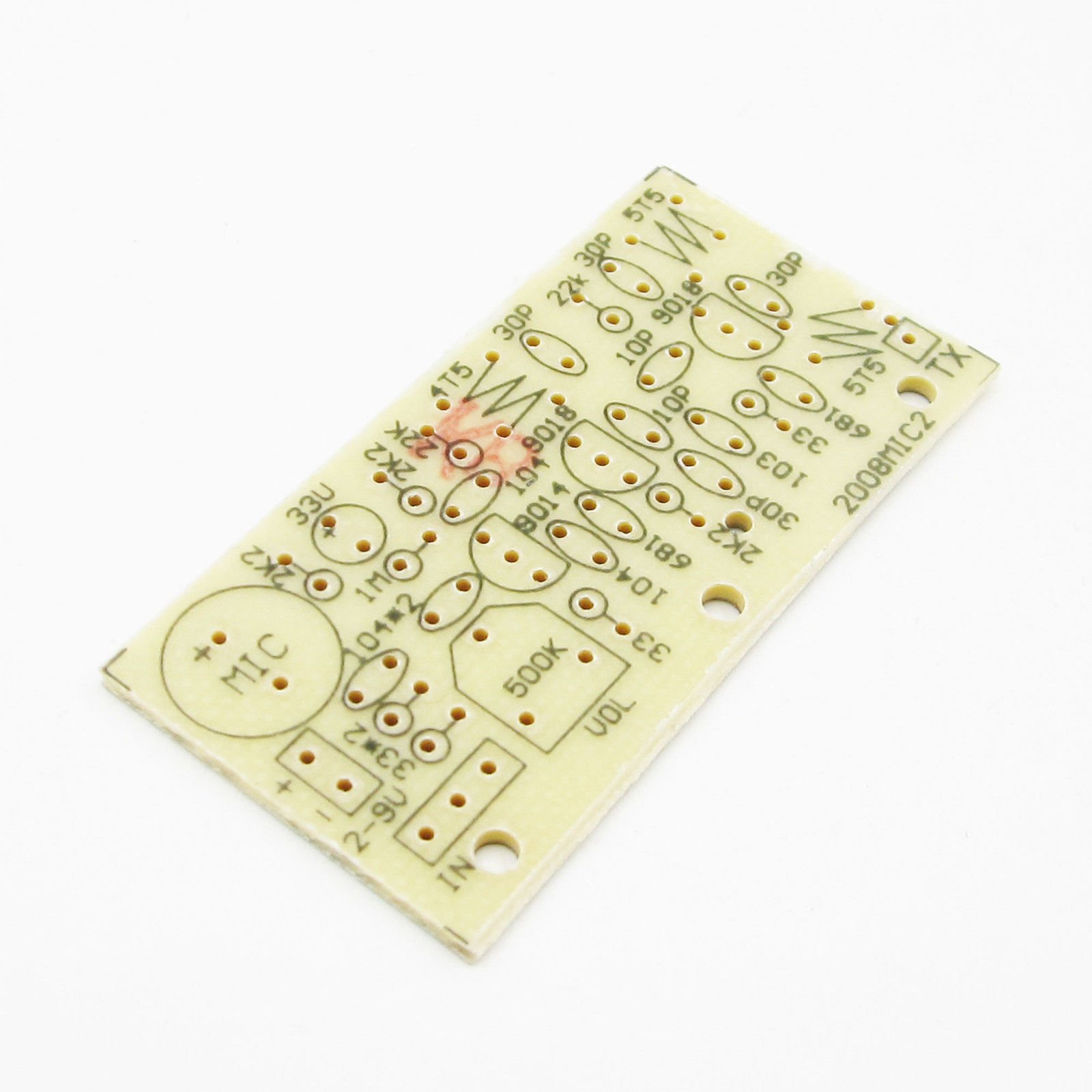
This is yet another FM transmitter DIY kit for beginners and hobbyists. It is slightly different from our previous FM transmitters. It has 3 NPN transistors and the transmission range is around 50-100 meters. It is an enhanced wireless microphone with excellent transmission quality. The voice transmitted by the microphone can be heard using an…

TSIR04 is a USB relay with optically isolated inputs and OLED display and temperature sensor port. It allows computer control switching of external devices by using the USB port of your computer. The communication medium also can be changed easily. Replace the USBBee module with a WiFiBee, it becomes a WIFI relay. It will be a Bluetooth relay when…

This is the second time I am writing an article on how to use the fully assembled clap switch that I designed in 2014. This time, I have put several images and written explanation on each of the images so that you can use it easily. At the end of the photo gallery, you can…
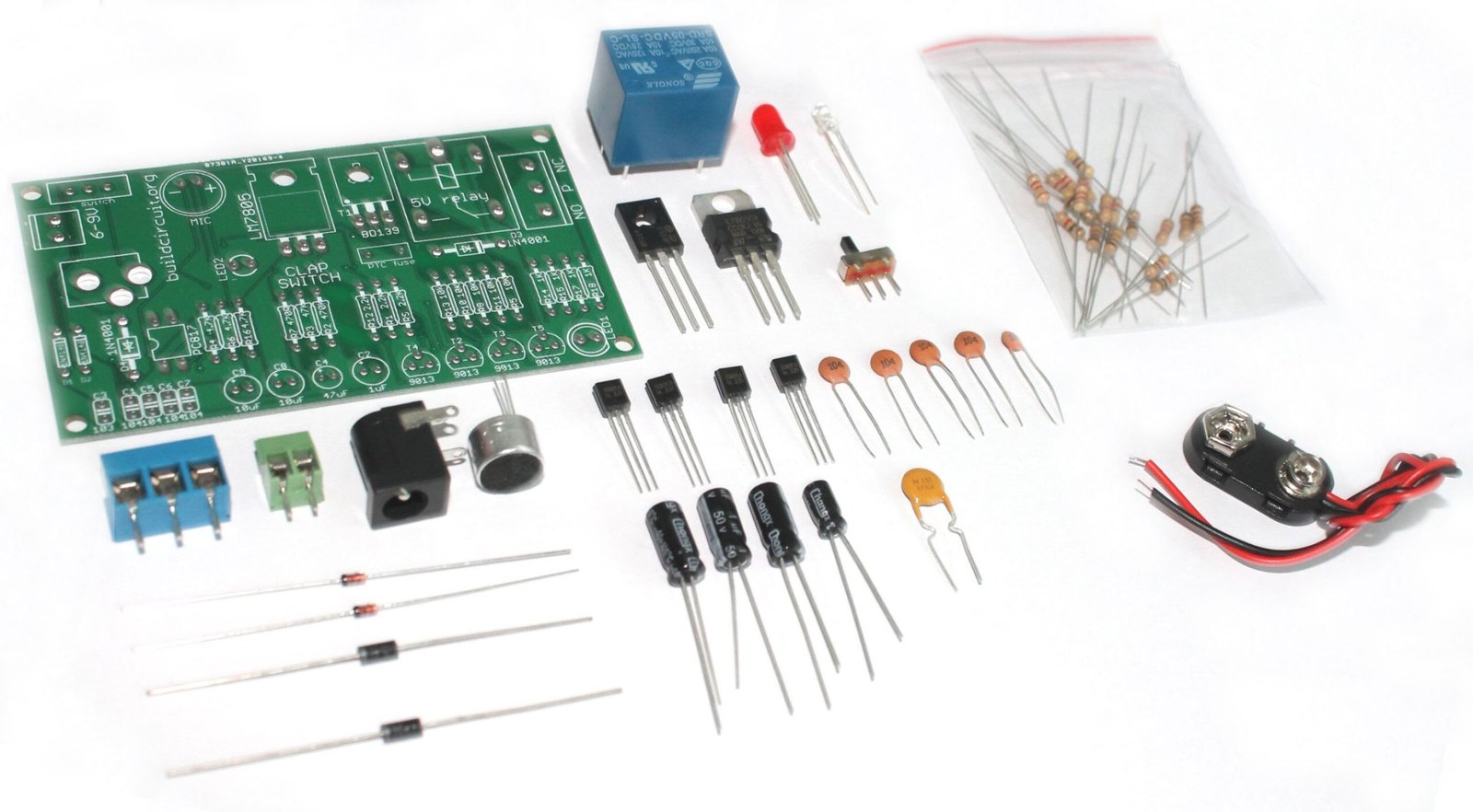
We are now selling fully assembled CLAP SWITCH(shipped from Sydney, Australia). Click here to visit the product page. If you have come to this page from a search engine, we recommend you to visit the page about DIY clap switch. In this article, we are going to describe how you can use the “do-it-yourself(DIY) clap…
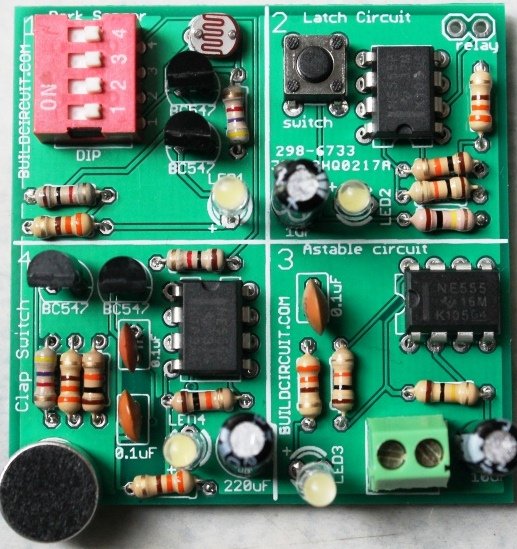

Just started electronics ? And you don’t know any engineering behind your projects and you are afraid of failure ? Then, this article can help you get started in electronics. Usually, success in initial projects plays important role in electronics amateurs and engineering students’ career. Many students quit electronics because they fail in their first,…
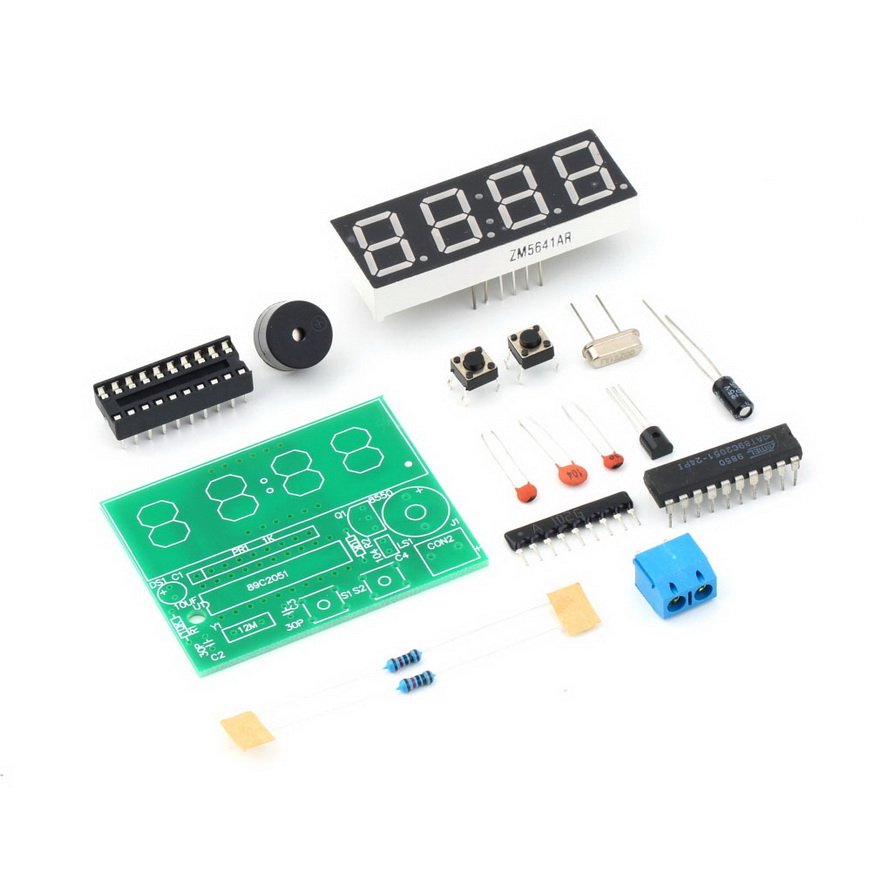

This is a very popular digital click for beginners. It is a DIY Kit. It is now available at BuildCircuit Store. It is based on AT89C2051-24PU. Basic Functions: 1. Hour and minute display & minute and second display 2. Two alarms set up There is a buzzer that works as an alarm. When the clock reaches…
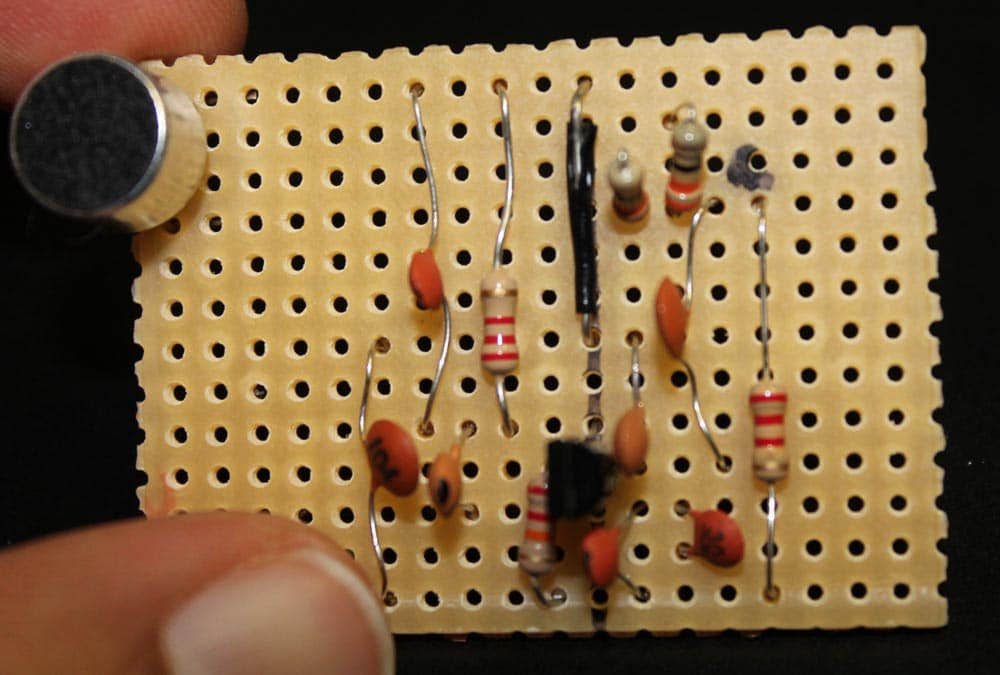
In this article, I am going to show how to plan and make a single transistor FM transmitter on a stripboard (prototype board). This project has been tested in a 5 storey building and it works perfectly well. You can transmit your voice or audio signals from your computer or music player to a distant…
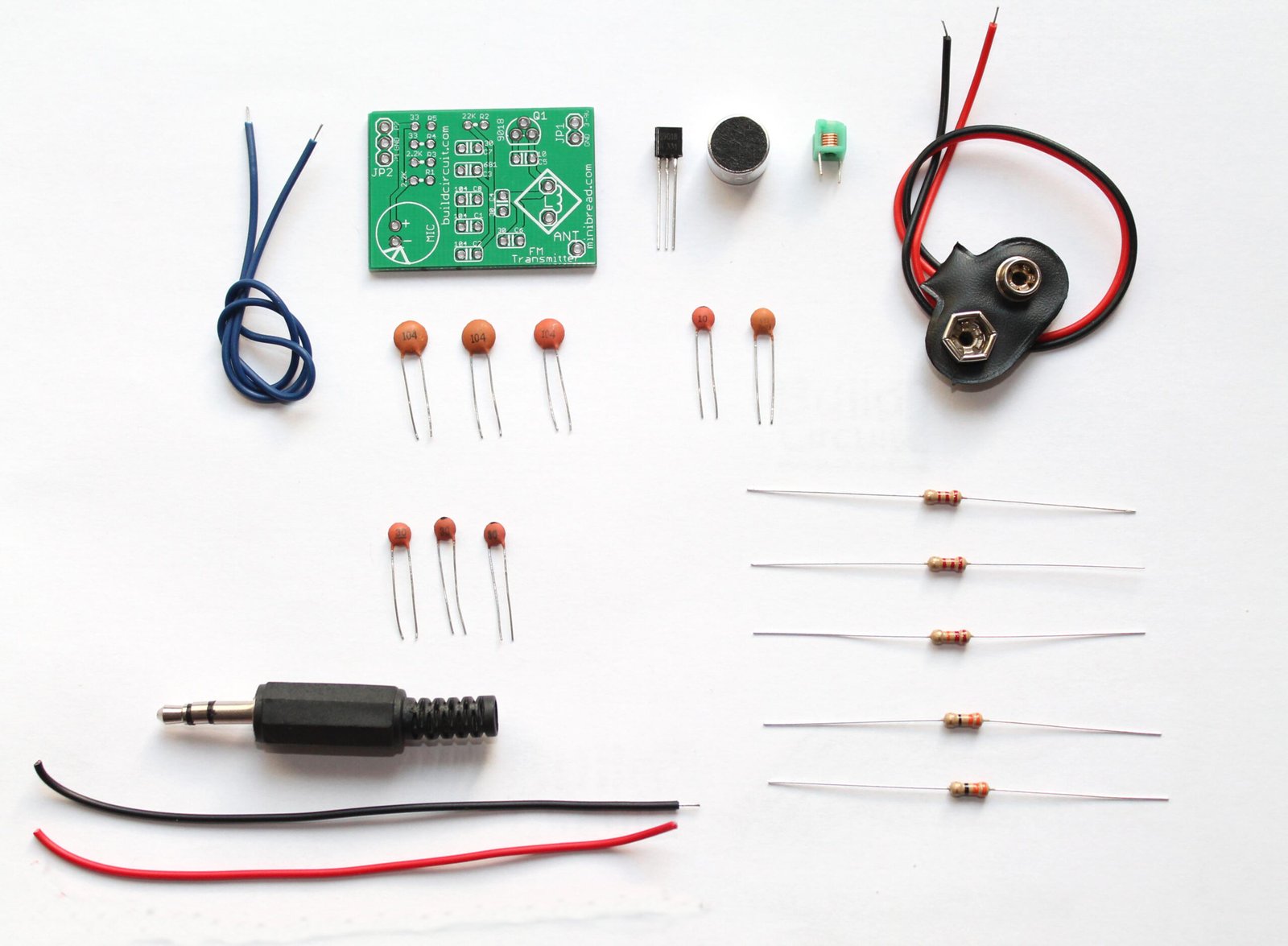
Here’s one of the easiest, simplest and the most popular FM transmitter for amateurs and electronics beginners. With this DIY kit, you can transmit your voice or audio over an ordinary FM radio within the FM broadcast band. It is a DIY kit designed by Sagar Sapkota. You can buy this kit at BuildCircuit Store….

This CSR USB-SPI programmer is the best suited kit for programming CSR series Bluetooth chips. It has much faster download speed than any other Parallel port programmer.
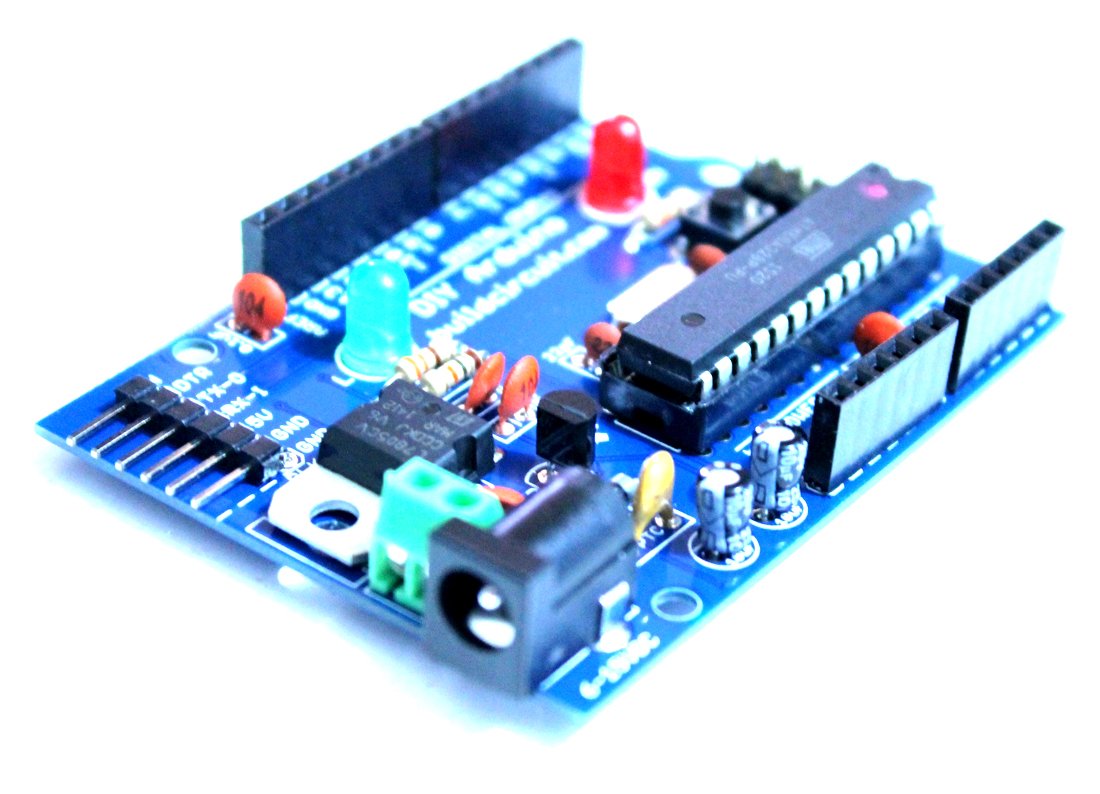
We are now selling BLUE colored DIY Arduino kit. You know that there are several versions of Arduino hardware. Hobbyists have also made Arduinos on strip boards giving different looks. Here’s one more Arduino, that is a simple do-it-yourself (DIY) kit. It is just like any other Arduino UNO board. However, it does not…

Change The BT module audio gains All of our Bluetooth audio amplifier boards and Bluetooth audio receiver boards use AudioB plus module as the core bluetooth receiver module. If you have to use a mismatch speakers or power supply in your system(size limit or other reasons). You may want limit the maximum output audio gains…

This is a MAX7456 OSD ( On Screen Display) shield for Arduino. The user can easily interrupt and overlay text and/or graphics onto a video signal (PAL or NTSC). It’s just about “plug-and-play” with an Arduino board. Plug this shield over Arduino main board and upload the given test sketch. Plug in your video signal to…

See page 1 Remaining part of assembly of line following robot… Fix the nut bolt set on the PCB Solder the photo resistor/LDR as shown on the image.Make sure that the LDR is at least 5mm above the ground or spot where you are placing the robot. Solder the transparent 5mm LEDs. The LEDs should…

The assembly of a line following robot is pretty straight forward. If you follow the silkscreen labels, you will be able to assemble it easily. The line following robot comes with the components as shown on the image. Start with resistors Solder all the resistors that comes with the package. Solder the transistors S8550 Solder…

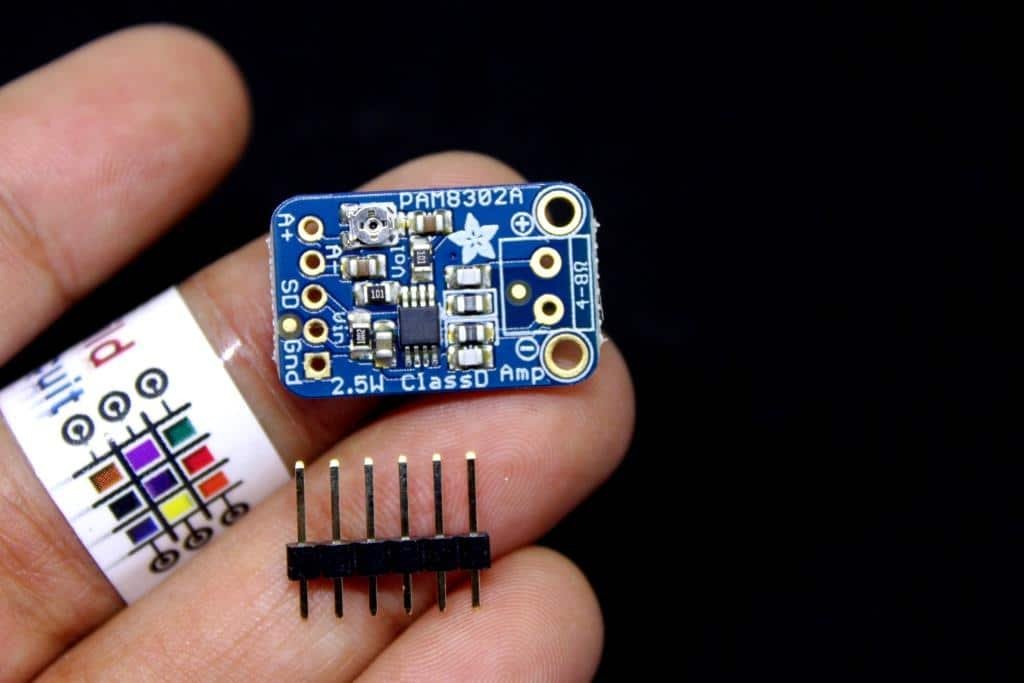
You can call this as an upgrade to LM386 based audio amplifier. We are also selling speakers for this module. This is a small but very powerful audio amplifier which is able to deliver 2.5 Watts into 4-8 ohm impedance speakers. It is based on Class D controller circuit that can be operated with 2.0V-5.5V DC….

A 3 pin NTC thermistor and LM393 comparator based module can be used to sense temperature or heat. It can be used both with and without Arduino. First, let’s see how you can use it with Arduino. Experiment: In this experiment, we simply increase the ambient heat around the thermistor and we’ll see how the…